June 6th marks the 81st anniversary of D-Day, an ideal opportunity to engage students in thoughtful discussions about World War II.
With Kialo, a free tool for class discussions, guide students through World War II topics to deepen their historical understanding while honing critical thinking and source analysis skills. Let’s take a look at some of the benefits of discussing history debate topics alongside some ready-to-go classroom resources.
Why are class discussions good for teaching students about history?
1. Students construct their own knowledge and build independent learning skills
In a Kialo discussion, students take the lead to actively shape conversations within a safe and supportive environment. This ownership motivates them to independently research, analyze, and organize information to build the discussion.
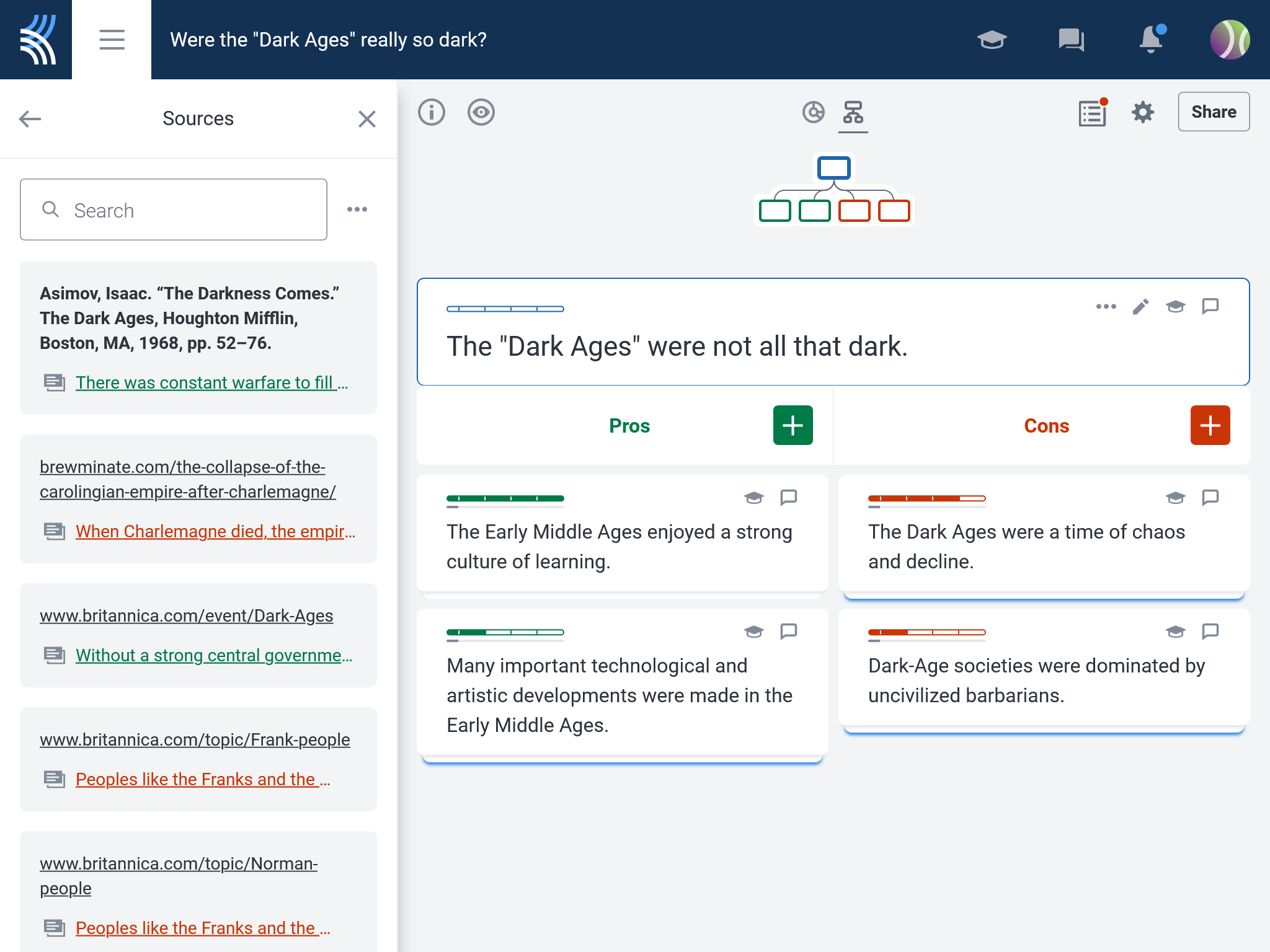
In doing so, students construct their own substantive knowledge from their respective starting points, with educators providing additional guidance as needed.
2. Students practice critical thinking through collaboration
In Kialo discussions, students can ask questions, challenge assumptions, and analyze different viewpoints. This process of collaborative inquiry fosters critical thinking skills, as students learn to evaluate evidence, consider alternative interpretations, and develop well-reasoned arguments.
3. Students develop an emotional connection to the topic, prompting deeper comprehension
Discussions on historical events give students the opportunity to more deeply explore the experiences of the people who were directly involved.
This fosters both a personal and emotional connection to the topic, motivating students to strengthen their understanding of these events and analyze their ongoing impact on people today.
Six engaging World War II discussion activities
1. Was the Treaty of Versailles the main cause of World War II?
Learning objectives:
- Students will be able to identify, analyze, and evaluate the relationship between multiple causes of World War II.
- Students will be able to compare and contrast long- and short-term causes of World War II.
Develop students’ understanding of causation by having them examine the Treaty of Versailles in this Kialo discussion, focusing on its relationship to World War I and its subsequent influence on World War II.
As they investigate the terms of the Treaty and its impact on Germany, students will deepen their understanding of the era’s political landscape and the multitude of factors that contributed to the outbreak of World War II.
Then, have students add claims to the Kialo discussion, comparing and contrasting the short- and long-term causes of the conflict. Students’ claims are displayed in a tree format, with connective lines showing the relationship between different causes.
This structure supports students in developing lines of reasoning, enabling them to draw informed conclusions on the main cause of World War II.
2. Could the Allied Powers have prevented World War II?
Learning objective:
- Students will be able to create relevant, structured, and evidentially supported accounts in response to the question.
Students can apply their knowledge of the causes of World War II to discuss whether the Allied Powers could have prevented the conflict. Start by recapping the political context and alliances of the era, clarifying the Allied and Axis Powers.
Next, have students conduct thorough research on whether the Allied Powers could have addressed issues such as Germany’s expansionism or economic instability more effectively to prevent the outbreak of war.
Then, students can use their findings to create a relevant, structured, and evidentially supported account — all within the discussion itself. They build their response by adding pro and con claims, while the branching discussion format helps structure their ideas.
Adding supporting evidence is much easier for students than in a traditional history essay: Once they locate a useful source (either online or offline), students simply link it to a claim and add a citation, ensuring their viewpoints are well-supported.
3. Should the US have entered World War II earlier?
Learning objective:
- Students will be able to make connections between one country’s perspective and international history.
Students can explore the connections between US priorities in the 1940s and international history by investigating the evolving position of the US before and during World War II. They will be able to analyze how leaders balanced domestic pressures, such as the public preference for neutrality, against the increasing international threat of Axis aggression.
When students collaborate in this discussion, they will see supporting and opposing arguments appear side by side, meaning they are consistently invited to engage with other perspectives. As differing perspectives may appear directly under a set of arguments, students are challenged to analyze their own as well as their peers’ positions.
4. Were the Nuremberg Trials effective in delivering justice for war crimes?
Learning objective:
- Students will be able to use sources to analyze the historical context of the Nuremberg Trials, considering bias, accuracy, and reliability.
For students to build a complete picture of World War II, they should also explore the consequences of the conflict, such as the Nuremberg Trials.
Students can use primary and secondary sources, including testimonies, recordings, and articles to analyze the historical context of these trials and engage with diverse perspectives on how people at the time perceived the trials.
Here, it’s important for students to explore the neutrality of the trials by critically assessing the source material for bias, accuracy, and reliability.
To encourage honest contributions on this sensitive topic, educators can make the discussion anonymous. This means students can add claims and comments via randomized usernames, with their real identities viewable solely by educators — removing students’ fear of judgment and maximizing the range of perspectives in the discussion.
5. Should the Allied Powers apologize for war crimes in World War II?
Learning objectives:
- Students will be able to contrast the consequences of war crimes for the Allied and Axis Powers.
- Students will be able to distinguish between long-term and immediate causes and effects of a historical event.
Studying the Nuremberg Trials may lead students to believe that the Allied Powers were innocent of war crimes. So, discuss how evolving perspectives have prompted the reassessment of certain Allied actions as potential war crimes.
Have students research controversial Allied actions, such as the bombing of Dresden and the atomic bombings in Japan. Then, students should compare these actions’ immediate and long-term causes and effects with those of Axis war crimes.
Students should then contrast the consequences that the Axis and Allied Powers faced. This research can inform students’ claims on whether the Allied Powers should now apologize for their actions.
To encourage thoughtful and respectful contributions from students, assign them a suggester role in the discussion.
This means educators must approve claims before they appear in the discussion, prompting students to reflect carefully on their ideas. Moreover, educators can address any misconceptions by using Grading and Feedback to give students individual feedback on their claims.
6. Did World War II significantly advance the rights of women in the countries involved?
Learning objective:
- Students will be able to use evidence to compare and contrast the long- and short-term effects of World War II on societal and gender roles.
Did World War II significantly advance the rights of women in the countries involved? — kialo-edu.com
In this discussion, students can explore the connection between military and social history, and gain insight into how past ideas and events can shape future ones.
They should use primary and secondary sources, such as diaries, letters, and historical analyses, to examine how women’s rights experienced short-term advancements during the war and evaluate if these rights were sustained in subsequent years.
Sources should reflect the experiences of women from diverse backgrounds, giving students an understanding of women’s experiences across different segments of society.
Whereas a traditional discussion on this issue may be dominated by a few students, in a Kialo discussion, everyone can contribute simultaneously, maximizing engagement. Moreover, because the discussion is automatically saved, your students can continue to add to it over time as their knowledge develops, and you can use it as assessment evidence!
Kialo’s World War II discussions are an accessible and engaging way to respectfully remember the D-Day anniversary with your students while building their critical thinking skills. What’s more, Kialo is completely free to use and integrate with familiar learning platforms.
Once you’ve seen the impact of these discussions, we’re sure that you’ll want to explore more discussion topics with your students! Simply head to our Topic Library which offers more than 600 free discussion prompts tailored to different age groups and curriculum subjects.

