Today’s accelerating technology means that there’s an accelerated spread of disinformation that reaches a much wider audience — including your students. Given that students are easily influenced by disinformation, it’s vital to equip them with media literacy skills and tools to critically evaluate content.
One of the most effective strategies to achieve this is lateral reading. So, let’s examine activities where students can use lateral reading to fact-check sources and fight disinformation.
What is lateral reading?
Rather than engaging in a deep, vertical read of a single source, lateral reading means that students quickly scan the content of a source, and then begin searching for additional materials to verify the information.
This contrasts with the vertical reading strategies associated with traditional print reading methods. Lateral reading is particularly suited to digital sources, which often combine different media formats, making traditional vertical methods less effective. Moreover, the lack of editorial control in online content necessitates the rigorous evaluation process that lateral reading provides.
How to read laterally
Students should use a structured approach when evaluating sources through lateral reading. Mike Caulfield’s SIFT method guides them through the process.
- Students should gain an initial overview of the source, then STOP to reflect on its potential reliability, making links to their existing knowledge. This helps students to develop an analytical — rather than emotional — response to the content and prepares them for the next three moves.
- Then, students should open multiple browser tabs and INVESTIGATE the source’s credibility. They should research the author and discover what other trusted sources say about the original source. This can help students judge the source’s reliability.
- Next, students should try to FIND the most reliable information on the topic. They can establish whether this new information supports or contradicts the original and gain additional perspectives on the topic.
- Finally, as sites often reuse content, students should TRACE information back to its original source to verify its accuracy within this new context.
Following this structured approach will enable students to evaluate the source effectively and result in a more comprehensive — and accurate — understanding of the topic.
Why is lateral reading important for students?
Lateral reading teaches students to efficiently evaluate sources
Lateral reading can prove more efficient than traditional verification methods. 1 Rather than spending time on in-depth vertical reading of potentially unreliable articles, students can use lateral reading to quickly grasp the topic and identify the most relevant and credible information from a range of sources, making research more accurate and productive.
Lateral reading develops students’ media literacy skills
Students use media to inform their actions and opinions, making media literacy skills vital. Through lateral reading, students compare different types of media sources on the same topic to distinguish between reliable and unreliable sources. With practice, they hone their ability to identify disinformation clues, develop a wider knowledge base to contextualize information, and build their own bank of reliable sources.
Lateral reading equips students with news literacy skills
Developing students’ news literacy skills through lateral reading is vital, given their reliance on social media as a news source. Lateral reading can broaden students’ understanding of the media, enabling them to understand what constitutes news and what doesn’t.
This helps them identify fact and opinion and to recognize agendas, sensationalism, and speculation present in the news. In doing so, students can build the healthy skepticism required to engage with digital news sources.
Lateral reading enables students to make better decisions
Using lateral reading enables students to become adept at fact-checking sources, which can lead to better decision making. The ability to differentiate between accurate guidance and harmful advice empowers students to make informed decisions that prioritize their own and others’ safety.
Lateral reading helps students reflect on diverse perspectives
Through lateral reading, students encounter a variety of diverse perspectives on a single topic. Evaluating these different viewpoints enables students to identify inaccurate or biased information. Moreover, this helps deepen understanding of a topic as encountering diverse perspectives can counteract confirmation bias, making students more likely to develop objective, informed viewpoints.
Lateral reading fosters students’ civic engagement
Exploring multiple perspectives through lateral reading helps students develop a more accurate understanding of important social issues. This can foster an open-minded approach when discussing controversial topics, which can bridge social divisions. Deepening students’ understanding of civic values and social justice in this way can encourage them to become active, engaged citizens.
Strategies for using lateral reading to evaluate sources
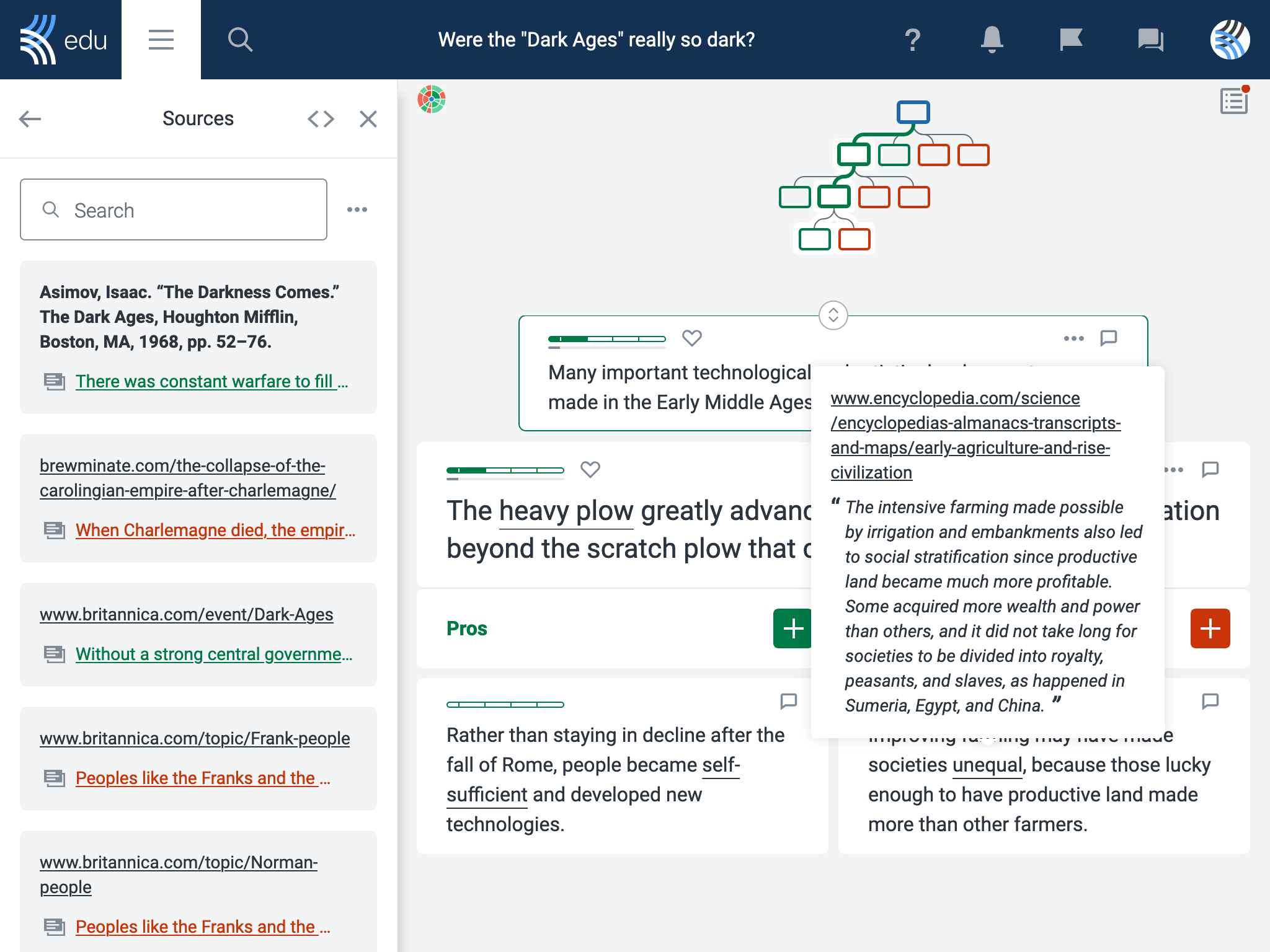
1. Search for various sources on the same topic to verify content
By searching for additional authoritative sources on the same topic, students can verify the consistency of information. Reading laterally like this also deepens their knowledge through exploring different perspectives.
For example, when exploring the best way to fight climate change, students may discover a host of contradictory information from fossil fuel companies, environmental action groups, and political organizations. Lateral reading can help students fact-check each organization’s claims.
Students can assess the author’s credibility by searching for other articles written by the same author. This can help students establish the author’s reputation as a trusted source.
3. Check how the information is funded to identify potential bias
Funding can influence the credibility of information, particularly in industry-sponsored studies. Where funders have a vested interest in the research, authors may manipulate data to align with the funder’s goal. Thus, students should always check funding details to establish reliability.
4. Use fact-checking websites for expert verification
Fact-checking websites can help students to verify information on their research topic. These platforms are operated by impartial experts trained to critically evaluate information.
With access to extensive resources and highly efficient verification methods, fact-checking platforms are well-equipped to help students identify disinformation.
5. Check other readers’ opinions to gain insights on source reliability
Other readers can provide valuable insights on the accuracy or credibility of a source through comments or chat. They may identify bias within the author’s arguments or conflicting information in other sources. Moreover, other readers may offer alternative perspectives that deepen students’ understanding of the topic.
Activities to practice lateral reading on Kialo Edu

A Kialo Edu discussion provides an ideal context for students to hone their lateral reading skills. Here’s how students can practice!
1. Research credible information to support claims
Students create robust arguments to support or counter a thesis. They then use lateral reading to research authoritative and credible supporting information that strengthens their claims.
2. Outline lateral reading strategies
When students link to a reliable source, they can outline their lateral reading strategies in the Quote/Note box. This facilitates educators in reviewing and giving feedback on students’ research methods.
3. Practice sharing credible sources and strategies
Students can collaborate on discussions, evaluating each other’s lateral reading strategies and sharing useful fact-checking resources in the Comments section.
4. Record lateral reading process on a Kialo Edu argument map
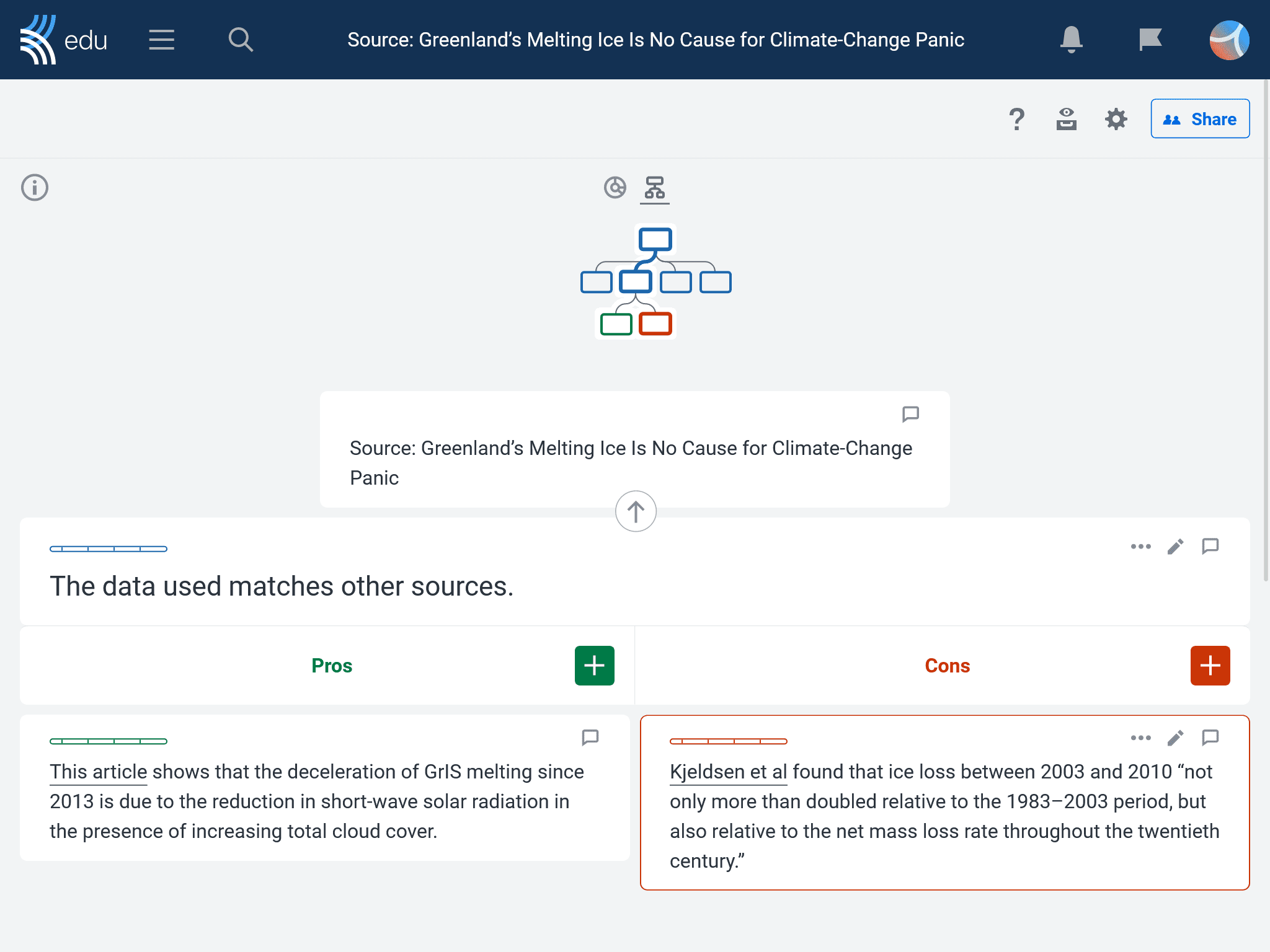
- Students add the main source as the thesis. Then, they include their evaluation notes from the lateral reading process as pros and cons.
- Students use this visual representation to analyze the reliability of the source, facilitating a final judgment on credibility.
The prevalence of disinformation suggests it’s here to stay. However, by regularly integrating research-based activities — like Kialo Edu discussions — into lessons, educators can ensure media literacy strategies like lateral reading become instinctive to students.
So, head to our topic library, select a curriculum-linked discussion, and begin training your students’ media literacy skills to fight the battle against fake news and disinformation!
We would love to hear how you’ve used lateral reading to improve your students’ media literacy skills and combat disinformation. Contact us at feedback@kialo-edu.com, or share your ideas on any of our social media platforms.
Footnotes
- Wineburg, S., & McGrew, S. (2017). Lateral Reading: Reading Less and Learning More When Evaluating Digital Information. Stanford History Education Group Working Paper No. 2017-A1. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3048994

